Intermittent Fasting: Benefits, Myths, and How to Get Started
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained significant attention in recent years as a popular approach to weight management and overall health. This guide explores the benefits of intermittent fasting, debunks common myths, and provides practical tips on how to get started.
Table of Contents
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. Unlike traditional diets, which focus on what you eat, IF focuses on when you eat. There are several popular methods of intermittent fasting:
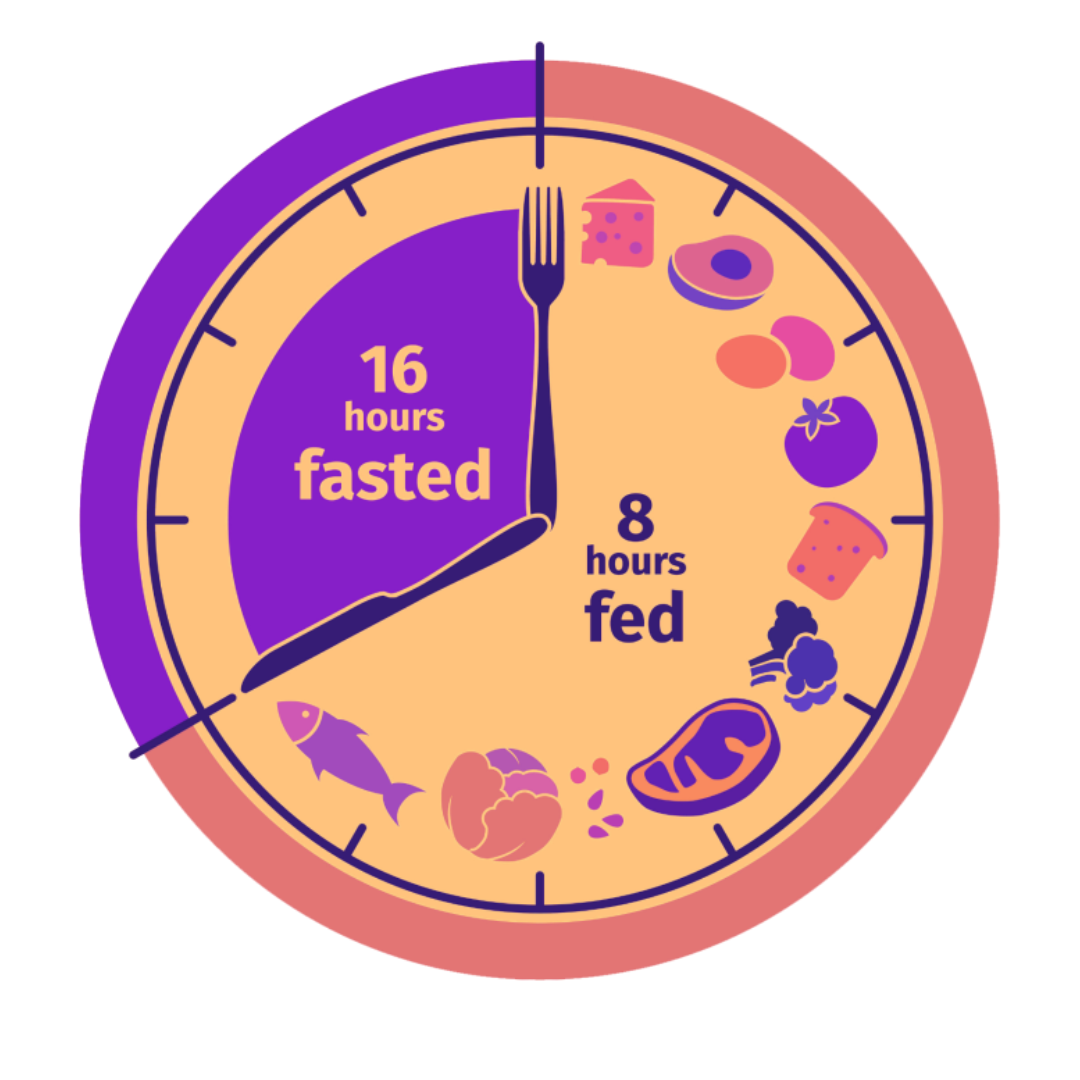
- 16/8 Method: Fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window.
- 5:2 Diet: Eat normally for five days a week and restrict calorie intake to 500-600 calories on the other two days.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: Involve 24-hour fasts once or twice a week.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Alternate between days of normal eating and fasting.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
- Weight Loss and Fat Loss: By reducing the eating window, intermittent fasting can naturally lead to a reduction in calorie intake. Additionally, fasting periods can increase the levels of norepinephrine, a hormone that boosts metabolism.
- Improved Metabolic Health: Intermittent fasting can improve several metabolic markers, including insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels. It helps reduce insulin resistance, lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Enhanced Brain Function: Fasting can increase the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports brain health. It may also protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
- Cellular Repair and Longevity: During fasting, cells initiate autophagy, a process that removes damaged cells and regenerates new ones. This can enhance cellular repair and may contribute to longevity.
- Reduced Inflammation: Studies suggest that intermittent fasting can reduce markers of inflammation, which are linked to various chronic diseases.
Common Myths About Intermittent Fasting
- Myth: Intermittent Fasting Causes Muscle Loss
- Truth: When done correctly, intermittent fasting primarily burns fat stores and preserves muscle mass. Incorporating strength training and adequate protein intake can further prevent muscle loss.
- Myth: Fasting Leads to Binge Eating
- Truth: While some people may overeat initially, most find that their appetite adjusts over time. Mindful eating and balanced meals can help prevent bingeing.
- Myth: Fasting Slows Down Metabolism
- Truth: Short-term fasting can actually boost metabolism by increasing norepinephrine levels. Prolonged fasting may have the opposite effect, but this is typically not the case with intermittent fasting.
- Myth: Intermittent Fasting is Only for Weight Loss
- Truth: While weight loss is a common benefit, intermittent fasting also offers numerous health benefits such as improved metabolic health, enhanced brain function, and reduced inflammation.
How to Get Started with Intermittent Fasting
- Choose a Method: Select a fasting method that fits your lifestyle. The 16/8 method is often recommended for beginners due to its simplicity.
- Ease into It: Start by gradually increasing your fasting window. For example, if you typically eat over a 12-hour window, try reducing it to 10 hours, then 8 hours over a few weeks.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water during fasting periods to stay hydrated. Herbal teas and black coffee are also allowed.
- Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: During eating windows, prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods such as vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to intermittent fasting. If you experience extreme hunger, fatigue, or other adverse effects, consider adjusting your fasting schedule or consulting with a healthcare professional.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of intermittent fasting. Stick to your chosen method and allow your body time to adapt.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting can be a powerful tool for improving your health and achieving your fitness goals. By understanding the benefits, dispelling common myths, and following practical tips for getting started, you can make intermittent fasting a sustainable part of your lifestyle. As always, consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your eating patterns, especially if you have underlying health conditions.