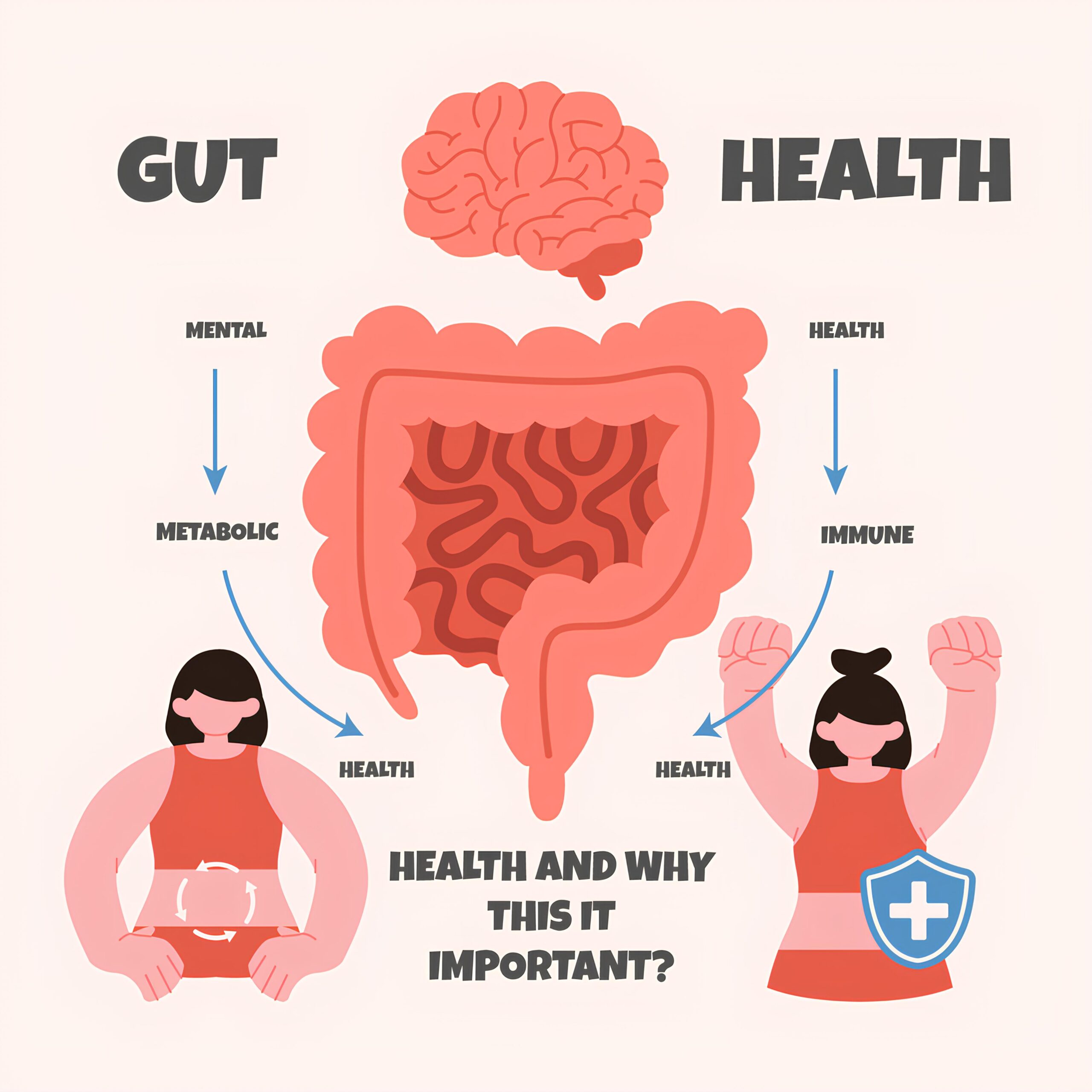
Within recent past, well-being has centered mainly on the gut significantly due to its importance. The gut is often called ‘second brain’ and among other functions; it aids in digestion and mental health among others. In this article we highlight why gut health matters, what can affect it and ways to keep your gut healthy.
Table of Contents
The Gut Microbiome: A Complex Ecosystem

Our digestive tract hosts trillions of microorganisms, comprising a complex community commonly known as the gut microbiome. The involved microbes are indispensable for human health due to the numerous functions they carry out. Such functions include breaking down intricate carbohydrates, producing vital vitamins, as well as modulating the immune system. Furthermore, these gut microbial colonies communicate with the brain via a bi-directional highway called the gut-brain axis that affects our moods, stress levels and cognitive processes.
The Importance of a Balanced Microbiome
Maintaining good health can be assisted by a balanced gut microbiome. Such an imbalance may result in dysbiosis, which is a condition when an imbalance of microorganisms occur in your gut. Dysbiosis has been linked to several health problems, including digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease, metabolic conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, and mental health issues including anxiety and depression.
Recent research has highlighted the connection between gut health and various aspects of overall well-being:
1)Digestive Health: A well-functioning gut microbiome is responsible for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients. Moreover, it is essential for guarding the gut’s lining against inflammation and infection. An unbalanced gut flora may result into various digestive disorders like bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea.
2)Defense Capability of the Body: Almost seventy percentage of our defense capability is situated in energy systems. Maintained balance among life forms colonizing the intestines help aid inflammation management hence increasing bodies’ capability to resist invading germs. On the contrary, disturbances in intestines populated with different microorganisms may cause high chances towards infection and autoimmune ailments.
3)Emotional Wellness: Gut brain axis represents one form of connection between our intestines or tummy and brain. Therefore, scientists are able to prove how gut status affects mental health disorders including depression as well as anxiety attacks. For instance, there are specific types of bacteria within the intestine that produce serotonin which act as neurotransmitters thereby changing our mood positively.
4)Metabolic Health: The gut microbiome affects metabolism and can influence weight gain or loss. Certain bacterial strains are associated with obesity, while others are linked to a leaner physique. The microbiome also affects how we metabolize food and store fat.
Factors Affecting Gut Health
Several factors can impact the health of your gut microbiome, including:
1)Diet: Food plays a major role in influencing your gut microbiome. A healthy microbiome is mainly promoted by diets that are rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables and fermented foods. On the other hand, processed foods diet, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to dysbiosis.
2)Antibiotics: Although they are important in treatment of bacterial infections, antibiotics can also disturb the balance of bacteria in the gut by killing both good and bad microorganisms together. The main consequences of these situations include what is commonly referred to as antibiotic-associated diarrhea as well as long-term disturbances in intestinal flora.
3)Stress: Gut functionality is adversely affected by chronic stress through alteration of intestinal motility and increased permeability. This situation causes “leaky gut” syndrome characterized by movement of toxins and microorganisms across the intestines into bloodstream which may give rise to inflammation and immune reactions.
4)Sleep: To keep your gut microbiome healthy you need quality sleep. Disrupted sleep patterns may damage your digestive system by resulting into imbalances in gut bacteria and therefore causing related problems.”
5)Physical Activity: Regular physical activity has been shown to positively influence the diversity and composition of the gut microbiome. Exercise promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria and helps maintain a healthy gut environment.
Tips for Promoting a Healthy Gut
Preserving gut health necessitates lifestyle and dietary adjustments that promote the microbiome’s well-being:
1)Eat a Diverse Range of Foods: A varied diet full of different types of dietary fiber together with fruits, vegetables and whole grains can promote microbial diversity in gut. Include in your meals several varieties of plant foods.
2)Include Fermented Foods: Fibrous bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut or even kombucha helps to have an advantage over the competitors by making them fit for the gut microbiome. If you are intersted iin buying kefir kindly click the link https://amzn.to/3M40qTB
3)Prebiotics: They are considered non-digestible fibers that help to feed beneficial bacteria found within gastro-intestinal tracts. Foods rich in prebiotics include garlic, onions, bananas and asparagus. If you want to buy prebiotics for gut health kindly click the link https://amzn.to/4e1OTAf
4)Limit Processed Foods and Sugars: Avoid processed foods as well as sugary snacks and artificial sweeteners since these can harm the intestinal flora and foster growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
5)Manage Stress: Support gut health by engaging yourself into activities meant to reduce stress levels such as meditation, yoga or deep breathing exercises.
6)Stay Hydrated*: Plenty of water helps keep mucosal lining of intestines intact and improves digestion overall. If you wanna get more hydrated consider buying this sugar free hydration packets https://amzn.to/3X4Gwy8

7)Get Enough Sleep*: Spend 7-9 hours sleeping every night so as to boost gut wellness alongside general good state of being.
8)Eat a Diverse Range of Foods: A varied diet rich in different types of dietary fiber, fruits, vegetables and whole grains promotes microbial diversity within the gut system. Make an effort to eat various kinds of plant food.
If you want a complete guide on hoe to improve your gut health and how to live a pain free and great life consider checking out this book https://amzn.to/3Ar4Cu3

Conclusion
Gut health is essential to overall well-being, impacting everything from digestion to mental health. You can improve your overall health and well-being by appreciating the significance of the gut microbiome and adopting practices that promote a healthy gut. In order to maintain a healthy gut—and therefore a healthy body and mind—one needs for instance; a balanced diet, stress management, regular exercise as well as proper sleep.
FAQs
1. What are the indicators of an unhealthy gut?
Signs of a gut that is not healthy could be things such as bloating, farting, diarrhea constipation, sensitivity to some foods, fatigue and unintentional weight changes. Other indications could be chronic intestinal discomforts, frequent infections in the body and mood swings.
2. In what ways can I boost my gut health?
A person who wants to boost their gut health should consume a variety of fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Secondly, it is important to add fermented foods e.g. yogurt and kimchi to your meals while at the same time cutting back on processed food as well as sugary items. Also managing stress levels by drinking enough water and exercising regularly will create an enabling environment for good gut functioning.
3. Are probiotics required for a healthy gut?
Probiotics may promote good gut conditions because they can support the maintenance of biology diversity in the gut and digestive process. Although not everyone should use probiotic supplements; one can incorporate certain dietary sources like yogurt, kefir or other fermented vegetables which are loaded with microorganisms that favour gut well-being instead.


hi